310. Minimum Height Trees
題目
A tree is an undirected graph in which any two vertices are connected by exactly one path. In other words, any connected graph without simple cycles is a tree.
Given a tree of n nodes labelled from 0 to n - 1, and an array of n - 1 edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an undirected edge between the two nodes ai and bi in the tree, you can choose any node of the tree as the root. When you select a node x as the root, the result tree has height h. Among all possible rooted trees, those with minimum height (i.e. min(h)) are called minimum height trees (MHTs).
Return a list of all MHTs' root labels. You can return the answer in any order.
The height of a rooted tree is the number of edges on the longest downward path between the root and a leaf.
Example 1:
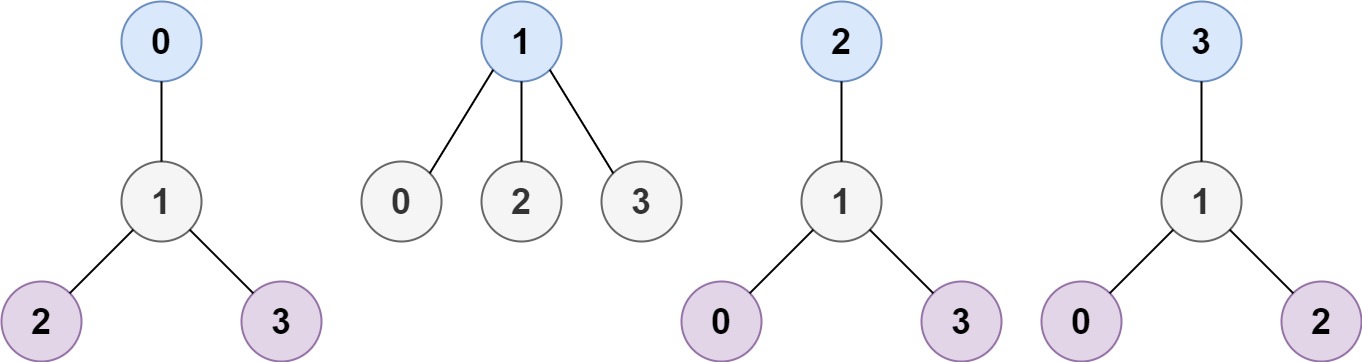
Input: n = 4, edges = [[1,0],[1,2],[1,3]]
Output: [1]
Explanation: As shown, the height of the tree is 1 when the root is the node with label 1 which is the only MHT.
Example 2:
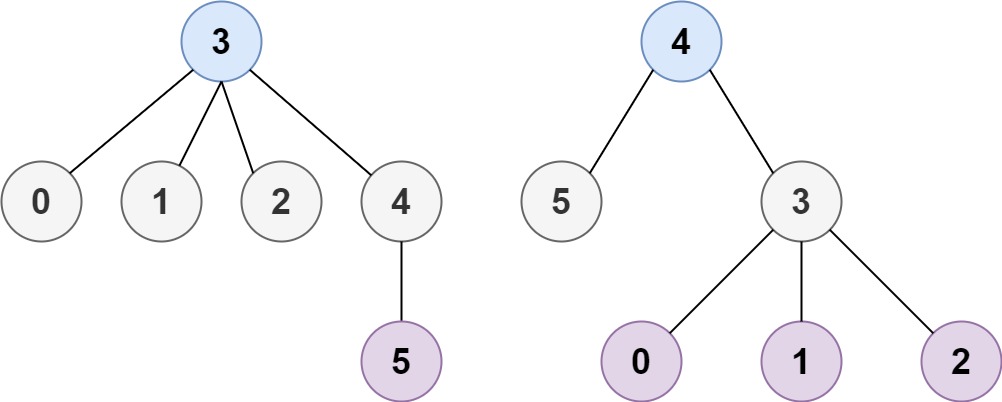
Input: n = 6, edges = [[3,0],[3,1],[3,2],[3,4],[5,4]]
Output: [3,4]
Constraints:
- 1 <= n <= 2 * 104
- edges.length == n - 1
- 0 <= ai, bi < n
- ai != bi
- All the pairs (ai, bi) are distinct.
- The given input is guaranteed to be a tree and there will be no repeated edges.
題目大意
輸入一個n個節點的二叉樹, 計算出最小高度(root到left的最短距離)
解題思路
用BFS來解. Queue 起點就是root, 終點就是最靠近root的那個葉節點(就是兩個子節點都是null)
來源
- https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-height-trees/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-height-trees/
解答
https://github.com/kimi0230/LeetcodeGolang/blob/master/Leetcode/0310.Minimum-Height-Trees/main.go
package minimumheighttrees
import "fmt"
func FindMinHeightTrees(n int, edges [][]int) []int {
if n == 1 {
return []int{0}
}
graph := make(map[int][]int)
degree := make(map[int]int, n) //出度: 出度是指從該節點(頂點)出發的邊的條數
// 建立對應關係
for _, v := range edges {
if _, ok := graph[v[0]]; ok {
graph[v[0]] = append(graph[v[0]], v[1])
} else {
// 沒找到
graph[v[0]] = []int{v[1]}
}
if _, ok := graph[v[1]]; ok {
graph[v[1]] = append(graph[v[1]], v[0])
} else {
// 沒找到
graph[v[1]] = []int{v[0]}
}
degree[v[0]]++
degree[v[1]]++
}
fmt.Printf("graph: %+v \n", graph)
fmt.Printf("degree: %+v \n", degree)
var queue []int
for key, value := range degree { //先找到出度為1的點, 加到Queue
if value == 1 {
queue = append(queue, key)
}
}
fmt.Printf("queue: %+v \n", queue)
leaves := []int{}
for len(queue) != 0 {
leaves = leaves[0:0]
size := len(queue)
for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
leaves = append(leaves, queue[i])
for _, neighbor := range graph[queue[i]] { // 將該點鄰接出度-1, 等於1時加入Queue
degree[neighbor]--
if degree[neighbor] == 1 {
queue = append(queue, neighbor)
}
}
}
queue = queue[size:]
}
return leaves
}
/*
n: 4, edges: [][]int{{1, 0}, {1, 2}, {1, 3}},
graph: map[0:[1] 1:[0 2 3] 2:[1] 3:[1]]
0 (degree: 1)
/
1 (3)
/ \
2(1) 3(1)
degree: map[0:1 1:3 2:1 3:1]
queue: [2 3 0] (先degree=1)
*/